Copyright © 2023 The Green Side. All Rights Reserved.
Website Managed By Ops Assist
Welcome to the beginning of the rest of your life.
This journey begins with one step.
You’re road to perfect health has begun.
Our Endcocannabinoid ‘ECS’ accredited coaching team is here to assist
We offer a variety of fresh and healthy, locally grown, organic fruit and vegetable boxes that are always seasonal, naturally fresh and always great value — delivered straight to your door.
We currently deliver in Gauteng and parts of Pretoria. We’ll constantly be growing and adding fresh and healthy products regularly so make sure to check in so you don’t miss out on the latest fresh goodness.
We offer a variety of fresh and healthy, locally grown, organic fruit and vegetable boxes that are always seasonal, naturally fresh and always great value — delivered straight to your door.
We currently deliver in Gauteng and parts of Pretoria. We’ll constantly be growing and adding fresh and healthy products regularly so make sure to check in so you don’t miss out on the latest fresh goodness.
We offer a variety of fresh and healthy, locally grown, organic fruit and vegetable boxes that are always seasonal, naturally fresh and always great value — delivered straight to your door.
We currently deliver in Gauteng and parts of Pretoria. We’ll constantly be growing and adding fresh and healthy products regularly so make sure to check in so you don’t miss out on the latest fresh goodness.
The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.

Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules made by your body. They’re similar to cannabinoids, but they’re produced by your body. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids so far: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG). These help keep internal functions running smoothly. Your body produces them as needed, making it difficult to know what typical levels are for each. 

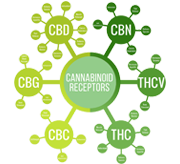
These receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to them in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects that result depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation, a common sign of autoimmune disorders.

Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG

Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG

The use of medical cannabis could ease the symptoms and help treat your condition
Book A Free Consultation!The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.

Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules made by your body. They’re similar to cannabinoids, but they’re produced by your body. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids so far: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG). These help keep internal functions running smoothly. Your body produces them as needed, making it difficult to know what typical levels are for each. 

These receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to them in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects that result depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation, a common sign of autoimmune disorders.


Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG


Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG

The use of medical cannabis could ease the symptoms and help treat your condition
The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.

Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules made by your body. They’re similar to cannabinoids, but they’re produced by your body. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids so far: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG). These help keep internal functions running smoothly. Your body produces them as needed, making it difficult to know what typical levels are for each. 

These receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to them in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects that result depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation, a common sign of autoimmune disorders.


Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG


Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve carried out their function. There are two main enzymes responsible for this: fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down AEA and monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which typically breaks down 2-AG

The use of medical cannabis could ease the symptoms and help treat your condition
Copyright © 2023 The Green Side. All Rights Reserved.
Website Managed By Ops Assist
Copyright © 2023 The Green Side. All Rights Reserved.
Website Managed By Ops Assist